Ultrasound capsules
Femoral nerve block and its iliac fascia variant


FI Block / Femoral Block - Key Points (local anesthetic volume)
Total volume to use: ~ 40 mL (Anesthetic + sterile NS)
Please refer to the 'medication' section to calculate your local anesthetic doses.
Dilute the anesthetic volume with sterile NS to a total volume of approximately 40 mL or maximum dilute the local anesthetic half and half.
Example: If I use 15 mL of ropivacaine 0.5% due to my patient's characteristics, I will dilute with 15 mL to total 30 mL and not 40 mL.
Clinically, there is very little/no difference between the two variants (FI vs femoral).
The diffusion of the anesthetic aims to reach 3 nerves:Femoral
Lateral cutaneous femoral
+/- Shutter
**Simple 2-step femoral block**
🟩 1
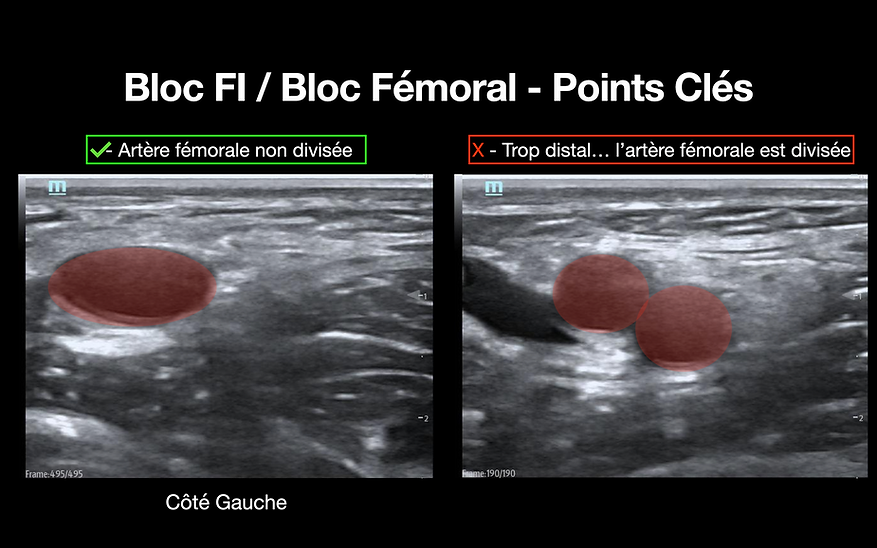
Identify the femoral artery and ensure that it is not divided
🟩 2
Swipe sideways and identify the Illiaca fascia starting from the bottom of the screen
FI Block / Femoral Block - Key Points (technique)
• Perform the block distal to the inguinal ligament, but proximal to the division of the femoral artery into the deep and superficial femoral arteries.
• The most reproducible way to identify the iliac fascia is by identifying the first fascia starting from the bottom of the screen and working upwards.
In my experience, identifying the two 'pops' as the fascia lata and iliaca leads to more confusion and errors.
• The femoral artery has a triangular fat pad directly lateral to it that often mimics the femoral nerve. However, the fat pad will be above the iliac fascia versus the nerve being below.
**It is not necessary to identify the femoral nerve for this block. We simply want to deposit the volume under the iliac fascia and it will diffuse towards the nerve.**

Femoral Block - Finalization of the block
• Once the needle is positioned as shown in the image below, simply inject the 30-40 mL into the same location.
• At this point, there is no point in changing the position of the needle since the diffusion of the liquid across the plane will take care of everything.
• It is still necessary to always keep the tip of the needle in sight and to apply negative pressure (aspiration) every 5mL. Safety first!


Ultrasound example


Video example (Femoral)

Video example (Fascia Iliaca)
